Tube Block
Treatments
- Fertility Surgery
- Microbiome Investigation
- Blastocyst Transfer
- ICSI
- Laser Assisted Hatching
- Donor Program
- G-CSF Installation
- Fertility Booster Diet
- Weight Loss Management
- PRP Instillation
Fertility Surgery
What is it?
A corrective surgery advised for the patients having structural abnormality of reproductive organs so as to improve the chances of conception. It can be for the male or the female partner.
How is it done?
First, minimal invasive diagnostic techniques are used to identify the problem and then a suitable surgical procedure is performed to correct it. The protocol can shortly shown as follows :
Female:
- Reversal of Tubectomy (Tubal ligation). The patient who has already undergone tubectomy for avoiding further pregnancies if decides to have a baby, this kind of surgery can be a solution wherein the ligatured (closed) fallopian tube is reconnected.
- Reconnecting fallopian tube: If there is blockage in fallopian tube due to some infection and pregnancy is not happening because of this, the tube can be reconnected surgically to solve the problem. It involves insertion of a small tube through cervix, uterus and connect the fallopian tube. The surgery is called Salpingostomy, sometimes called neosalpingostomy (the fallopian tube may be cut completely to open the passage for egg cells) or fimbrioplasty (when the tip of fallopian tube that is very close to ovarian is blocked, the tip if surgically opened).
- Polypectomy: A polyp is an abnormal collection of tissue. A polypectomy is a surgical procedure to remove polyps from the from an organ like Uterus. The procedure is relatively noninvasive and is usually carried out at the same time as a hysteroscopy.
- Myomectomy: This procedure sometimes also known as fibroidectomy, refers to surgical removal of uterinefibroids (leiomyomas). In comparison to hysterectomy, the uterus remains preserved in this procedure and the woman retains her reproductive potential.
- Dilatation for treating cervical stenosis: Cervical stenosis means a conditions wherein the cervix becomes extremely narrow. The treatment for this condition is using a dilator.
- Adhesiolysis: Some times, pelvic adhesions are observed blocking passage between uterus and ovarian. In such conditions natural pregnancy becomes difficult and even in ART oocyte pickup is obstructed by the adhesions. This disorder is treated by microsurgical technique or laparoscopic surgery to remove the adhesion and prevent its recurrence.
- Metroplasty: Sometimes, uterus is abnormal in shape such as ‘T’ or heart shaped and hence, can lead to complications during and after pregnancy. This condition is treated with metroplasty. The surgery involves reconstruction of uterine chamber to make into normal shape. With the surgery, implantation of embryo and further development is possible.
- PCO Drilling: Polycystic ovarian can cause the female body produce excess of testosterone and insulin, leading to fertility problems. High testosterone levels can cause irregular menstrual cycles, prevent ovulation and hinder pregnancy. Ovarian drilling can cure this problem Ovarian drilling is a laparoscopic procedure performed under general anesthesia. This surgery is typically done on an outpatient basis with minimal recovery time. With a laparoscopic tool small openings are mad in ovarian.
- Ovarian cystectomy: Endometriomas or chocolate cysts are benign masses growing around ovarian and obliterate the normal process of ovulation. Removal of these cysts is called cystectomy. The surgery needs to be done very carefully as there is a possibility of damage to ovarian vascular supply. Further, there is some decline in ovarian functioning after surgery. So, ART may be necessary for pregnancy.
Male:
- Treat varicocele(swelling of veins coming of Testis) which will allow testes to produce better sperms.
- Removal of blockage in the Epididymis (tubular extension of testis responsible for activation of spermatozoa).
- Reversal of Vasectomy. This is done when the couple decides to go for pregnancy after vasectomy surgery.
- Removal of sperms from testis surgically in case of Azoospermia (Absence of sperms in Ejaculate).
Microbiome Investigation
What is it?
The results demonstrated existence of an endometrial microbiota that is highly stable during acquisition of endometrial receptivity. However, poor reproductive outcomes for in vitro fertilization patients is associated with pathological modification of its profile. This finding provides a novel microbiological dimension to the reproductive process.
How is it done?
Endometrial fluid and vaginal aspirate are investigated for studying the microbial composition. On the basis of these findings distinction was made as a Lactobacillus-dominated microbiota (>90% Lactobacillus spp.) or a non-Lactobacillus-dominated microbiota (<90% Lactobacillus spp.). Although the endometrial microbiota is not regulated hormonally during the acquisition of endometrial receptivity, the presence of a non-Lactobacillus-dominated microbiota in a receptive endometrium was associated with significant decreases in implantation [60.7% vs 23.1% (P = .02)], pregnancy [70.6% vs 33.3% (P = .03)], ongoing pregnancy [58.8% vs 13.3% (P = .02)], and live birth [58.8% vs 6.7% (P = .002)] rates.
When is it recommended?
Uterocervical microbial colonization has been suspected to influence conception rates, with possible causes including an association between cervical microbial species and a pre-existing uterine infection, or colonization of the endometrium or the embryo during transport through the colonized cervix. This kind of microbiota has a significant impact on reproductive outcome even in ART procedures. So, ART failure for no known reason makes it mandatory to examine the Uterocervical microbiota so as to eliminate this as possible reason for ART failures. Thus, the main purpose is to investigate the impact of vaginal microbiome composition on reproductive outcomes within the context of infertility treatments, and the implications this have on assisted reproductive technology procedures.
Blastocyst Transfer
What is it?
The embryo formation after fertilization involves a number of stages such as 2 cell, 4 cells, 8 cells stage, Morula and so on. Gradually, the cells become distinct as outer cells (Trophoblast) and inner cell mass (embryonic cells). There is a small cavity in between. This stage is called blastocyst. Usually, the protective covering of embryo (Zona Pellucida) is still intact. The blastocyst hatches out of this covering to get implanted into endometrial lining (Innermost covering of uterus).
Using this blastocyst (developed in laboratory) for embryo transfer in IVF technique is called blastocyst transfer (Blast transfer).
When is it recommended?
Blast transfer is recommended for those patients with one more of the following conditions.
- The patients of higher age (35 years or more).
- Repeatedly failed IVF cycles.
- Recipient patients (who are receiving eggs or embryos from donor).
- Those who don’t have the mental preparation for further IVF cycles.
What are the advantages?
- Higher success rates even for patients of higher age.
- Growth pattern of the embryo is established in the laboratory before implantation. So, the doctor has a clear understanding about progress of embryo after implantation.
ICSI
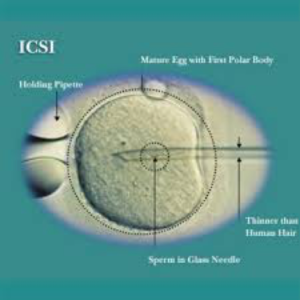
What is it?
It is a laboratory procedure where a single sperm is picked up with a fine glass needle and is injected directly into the egg. This is carried out in the laboratory by experienced embryologists using special equipment.
When is it recommended?
It is recommended in any or more of the following conditions.
- When the sperm count is very low
- When the sperm cannot move properly or are in other ways abnormal
- When sperm has been retrieved surgically from the epididymis (MESA/PESA) or the testes
- (TESE/TESA), from urine or following electro-ejaculation
- When there are high levels of antibodies in the semen
- When there has been a previous fertilisation failure using conventional IVF.
What are the advantages?
 Very few sperms are required for the process and the ability of the sperm to penetrate the egg is no longer important as this has been assisted by the ICSI technique. ICSI does not guarantee that fertilisation will occur as the normal cellular events like fusion of nuclei still need to occur once the sperm has been placed in the egg.
Very few sperms are required for the process and the ability of the sperm to penetrate the egg is no longer important as this has been assisted by the ICSI technique. ICSI does not guarantee that fertilisation will occur as the normal cellular events like fusion of nuclei still need to occur once the sperm has been placed in the egg.
Laser Assisted Hatching
What is it?
An embryo has a protective layer around it (zona pellucida) in early days of development. The process of implantation of the embryo begins on the fifth or sixth day after fertilization, when the embryo leaves its protective shell, zona pellucida disappears and the embryo cells get into direct contact with the cells of uterine wall (endometrium). This also causes elimination of a mechanical barrier which would impede further growth of the embryo.
Laser-assisted hatching: Using a specialized laser to breach the zonapellucida is another possibility. Laser-assisted hatching allows much more control of the size of the hole created. Laser assisted hatching is safest and most effective.
How is it done?
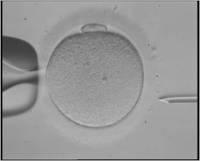
Problems with recurrent implantation failure may be caused by the embryo’s inability to “abandon” its protective shell or by the changes in the protective layer. In such cases, we perform the assisted hatching. In this technique we disrupt the hard shell of the embryo by laser (laser assisted hatching) or by a special needle(assisted hatching), just before the transfer. Thus we make it easier for it to attach to the uterine wall.
How do Embryos hatch naturally?
The oocyte (egg) before fertilisation has a protein-shell surrounding it known as the zona pellucida. The zona pellucida has many functions in embryo development which, change as the embryo grows.
- Before the egg becomes an embryo, the zona pellucida fuses with sperm cells. This is the start of the fertilization process.
- Once a single sperm cell penetrates the shell and fertilizes the egg, the zona pellucida hardens. This prevents more sperm cells from entering the now-fertilized zygote.
- The hardened shell also helps prevent the embryo from implanting prematurely in the fallopian tubes (which would cause an ectopic pregnancy).
- It also keeps the many blastocyst cells together.
- As the zygote travels down the fallopian tube and develops into the blastocysts stage, the zona pellucida expands and begins to thin and deteriorate.
- Around day four of development, the zona pellucida cracks open and the blastocyst/embryo emerges, leaving behind the thin-protein shell. This is the embryo hatching process.
- Within a few days of hatching, the blastocyst implants itself into the endometrium.
When is assisted hatching recommended?
- For older women who have eggs with a harder shell.
- For repeated implantation failure.
- For frozen embryos.
Donor Program
What is it?
When the patient couples have problems in conceiving and if the problem is found in the quality / quantity of germ cells (Gametes), oocytes or spermatozoa or embryos are collected from suitable donor and used for ART.
When is it recommended?
It is recommended in following situations.
- If the female partner is not able to produce oocytes suitable for fertilization, oocytes can be received from a suitable (depending on blood group and other body features) donor female.
- If semen sample of the male partner does not contain any sperms (Azoospermea) or adequate number of sperms (Oligospermia) or properly motile sperms (Asthanospermea) or morphologically abnormal (Teratospermea), sperms are received from a suitable donor male.
- If gametes from both the partners are not suitable for fertilization and further implantation, preformed embryos formed by fusion of gametes from appropriate male and female donor are taken used for ART.
How is it done?
- When oocyte donation program is to be conducted, the healthy donor female is contacted and is given suitable hormone therapy for release for oocytes. These eggs can be used for IVF and then can be transferred into uterus of recipient who is also on hormone therapy.
- In sperm donor program, healthy and suitable male is contacted and his semen sample is collected on the same day when IVF is to be performed. The eggs collected from female partner are fertilized in vitro and used for fertilizing the oocytes.
- For embryo donation program, oocytes from suitable healthy female (who is on hormone therapy) are collected. On the same day, semen is also collected either from the concerned male partner or donor and is used for IVF. After fertilization, the embryo development is allowed to proceed for three or five days depending upon hormonal status of the recipient. The embryo in 8 cell stage or Blastocyst stage is used for transfer into recipient female’s uterus.
G-CSF Installation
What is it?
It means Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor also known as factor CSF 3. This factor plays a key role in formation of Neutrophils and stem cells. Normally certain tissues in the body can produce it in adequate volume. When the synthesis is not enough, it can lead to various disorders some related to reproductive system. The factor can be artificially introduced and is known to improve results of IVF treatments.
When is it recommended?
When IVF attempts are failing and the reason is diagnosed to be deficiency of CSF 3, this treatment is recommended. In these patients, even after during the IVF protocol endometrial lining does not attain thickness adequate (minimum 7mm) for implantation of transferred embryo. There is a very nominal percentage of females which face this issue. The G-CSF is capable of leading to thickening of Endometrial wall (innermost lining of Uterus).
How is it done?
A particular drug called Filgrastim (produced by recombinant DNA technique) is injected as intravenous or subcutaneous and it regulates formation of Neutrophils. This improves the possibility of IVF success because it enhances endometrial thickening required for implantation of embryo thus, improving success rate of embryo transfer in IVF.
Fertility Booster Diet
Intake of proper food becomes very important during the fertility treatment. Eating certain foods during different phases of your menstrual cycle can enhance the fertility. So, if a woman wants to maximize her chances of conceiving, it is possible to eat foods that have advantageous to each phase. So, we ask our experts to weigh in on what to actually eat during each of the reproductive phase.
The list includes:
1. Plenty of fruits and vegetables
2. Complex carbohydrates – whole grains like brown rice , oats and whole meal bread .
3. Organic food where possible.
4. Oily foods like nuts, fish and oil.
5. Add lemon , pomegranate, green leafy vegetables and tomatoes to diet .
6. Flax seeds + sunflower seeds .
7. Avoid trans fats.
8. Increase intake of fibre.
9. More fish and organic eggs than red meat .
10. Avoid additive ,preservatives and artificial sweetner.
11. Reduce and avoid sugar both on its own and hidden in food .
12. Avoid caffeine : coffee, chocolate ,tea ,cola & alcohol .
13. Avoid processed food.
14. Try having fresh and home-made food.
Weight Loss Management
What is it?
It is avoiding weight gain or losing weight for improving the chances of conceiving. Too low or too high body weight can interfere with fertility of an individual and hence, needs to be managed appropriately.
How is it done?
Normally, weight loss management involved diet and exercise. The couple trying for pregnancy needs to take careful measures in this. Proper diet and moderate exercise are best recommended for weight loss. But during pregnancy if necessary, weight management must be done preferably by diet control. Heavy exercise can affect the embryonic development in uterus and hence, has to be avoided.
When is it recommended?
Excess body weight in female partner is known to reduce the possibility or pregnancy. There is a need to manage the weight appropriately for natural pregnancy or even IVF. When an obese patient approaches for IVF treatment, before treatment the patient needs to undergo weight management regime and only then the IVF protocol can be followed. As mentioned above, the weight loss should be by controlled diet and not entirely by exercise.
PRP Instillation - Platelet Rich Plasma
What is it?
It’s the plasma separated selectively from peripheral venous blood and enriched with activated platelets.
How is it done?
- It is plasma separated from freshly drawn whole blood from peripheral veins and stored in Acid Citrate Dextrose solution as anticoagulant.
- Various factors of blood are separated through activated platelets.
- Certain factors become bioactive and are secreted in 10 min after clotting. These factors are helpful in regulating cell migration, attachment, proliferation and differentiation, and also promoting extracellular matrix accumulation.
- The active platelet enriched plasma is infused into uterine cavity so as to enhance endometrial thickening.
- It has been known to stimulate the development of new tissue, making the uterine lining grow thicker in women with thin uterine linings. Thus, PRP can increase the success rate of IVF
When is it recommended?
The women with one of more of the following issues are recommended this treatment.
- Under age 40 who suffer from so-called primary ovarian insufficiency (POI).
- Those suffering with premature ovarian failure (POF) or premature menopause.
- Those who require ovarian rejuvenation for ART to be successful.
